Cannabis terminology in plain language
The world that revolves around cannabis has its own language, and for the uninitiated it can be a little intimidating at the start of a cannabis journey. No one likes to feel like a newb when you go to the local dispensary. To help you bypass the feeling that you missed something along the way, I offer some basic definitions as they pertain to cannabis and cannabis products.
This is by no means an inclusive list- just the highlights, the terms you’re most likely to come across as you begin to explore allowing cannabis to enhance your lifestyle.
Absorption – The uptake of ingested or administered food or medicine. You eat food or take medicine. In order for you to benefit from those actions your body breaks it all down into usable molecules and absorbs it.
Administration Methods – The many ways to introduce a medicine into the body, also known as dosing methods. Cannabis products are profoundly diversified, allowing cannabinoids and their component partners to be administered as:
- topicals
- edibles
- combustibles
- vapors
- patches
- and more…. There seems to be no end to the creativity of product development for efficiently administering cannabis to the broader population.

Bioavailability – The amount of components you consumed that your body will actually have access to after it’s been absorbed. Among the things that can influence bioavailability of cannabis for better or worse are:
- the administration method you choose
- how healthy you are
- what mood you’re in
- what you ate last, and when you ate it
- how comfortable you are with your setting and companions
In most cases, bioavailability is significantly lower than the administered dose.
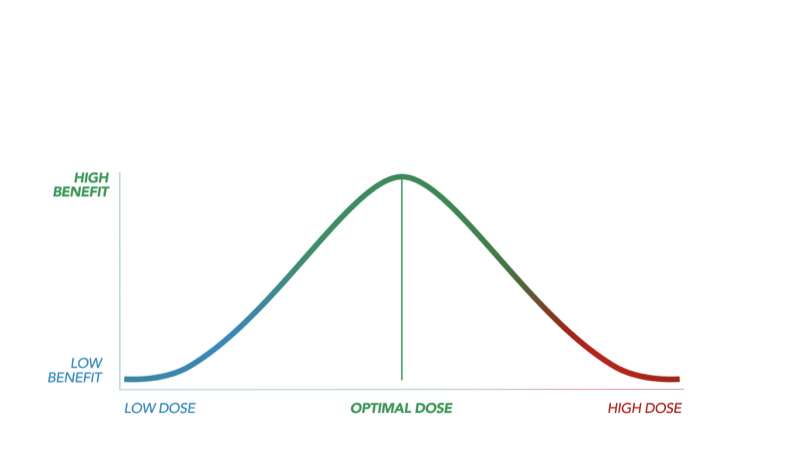
Biphasic – A biphasic medicine can have two completely opposite effects, depending on the dose you take.
Buds – The individual flowers of cannabis are tiny and stack right on top of each other as they mature and bloom. Our common name for those stacked flower bunches, whether still growing or in their dried state, is “buds.”

Buzz – Euphoria brought on by cannabis. The “high” everyone talks about is really just feeling like it’s all gonna be alright. How “alright” you feel when using cannabis is entirely dependent on how much THC you consume.
The buzz is easily controlled by:
- managing your dose of THC to a level you find comfortable
- balancing THC in ratio to CBD
Cannabinoids – Cellular signaling molecules used by the body to modify internal atmospheres of cells to keep it all in balance, so you can keep thriving. Cannabinoids can either be produced:
- by your own body (endocannabinoids)
- by plants, like cannabis
Now that we’re looking, other plants are being found that also produce cannabinoids, but none offer the incredible diversity cannabis produces. THC and CBD are the most abundant cannabinoids, but each cannabis plant can potentially produce dozens of different cannabinoids, all mixed together with other molecules like terpenes and flavonoids in an essential oil unique to that plant.
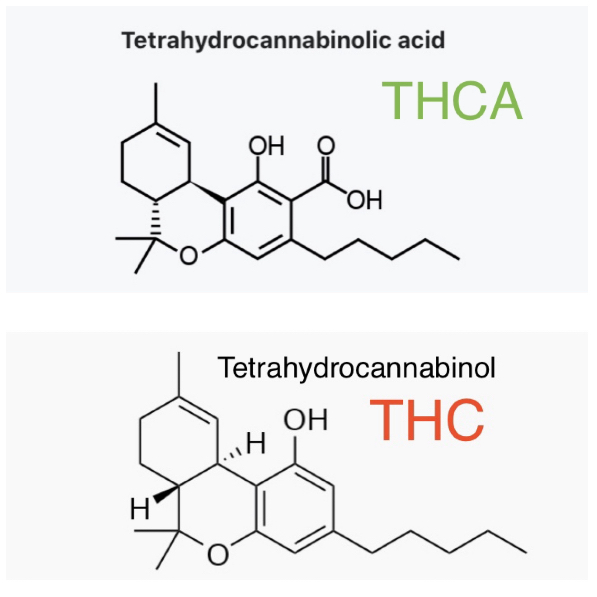
Cannabinoid Acids – AKA acid cannabinoids- these are the molecules actually produced by the cannabis plant. We decarboxylate cannabis plant material to transform the molecules into the neutral cannabinoids we’ve become more familiar with.
| Cannabinoid Acid (before decarboxylation) | Neutral Cannabinoid (after decarboxylation) |
| THCA | THC |
| CBDA | CBD |
| CBCA | CBC |
| THCVA | THCV |
Cannabis – AKA marijuana.

Cannabis Prohibition – The mysterious policy of lying to the public about the effects of the plant that made marijuana possession illegal, nearly ended the historic use of cannabis as a medicine, and created the ineffective, socially destructive monster we know as “The War On Drugs.”
Cannabis sativa L. – The noble and proper name for the plant we so lovingly call weed, pot, dope, ganja, chronic, etc. My personal choice for much of my adult life was “stuff,” as in, “Do we need to get some stuff before we settle in for the weekend?”
Combustion – Administration using a direct flame. Popular methods include smoking a joint, hitting a bong or firing up a bowl of buds in a pipe.
Concentrated Cannabis Oil (CCO) – Exactly what it sounds like, the extracted concentration of the essential oils of Cannabis sativa, often referred to as Rick Simpson Oil (RSO).
Concentrates – The name given to a variety of products made with concentrated oils, including, but not limited to, wax, shatter, and live resin.
Dabs – Hits of a high concentration of the essential oils of cannabis. Typically one uses a dab rig attachment or a specialized vaping pen for dabs.

Decarb – The popular shortened term for decarboxylation.
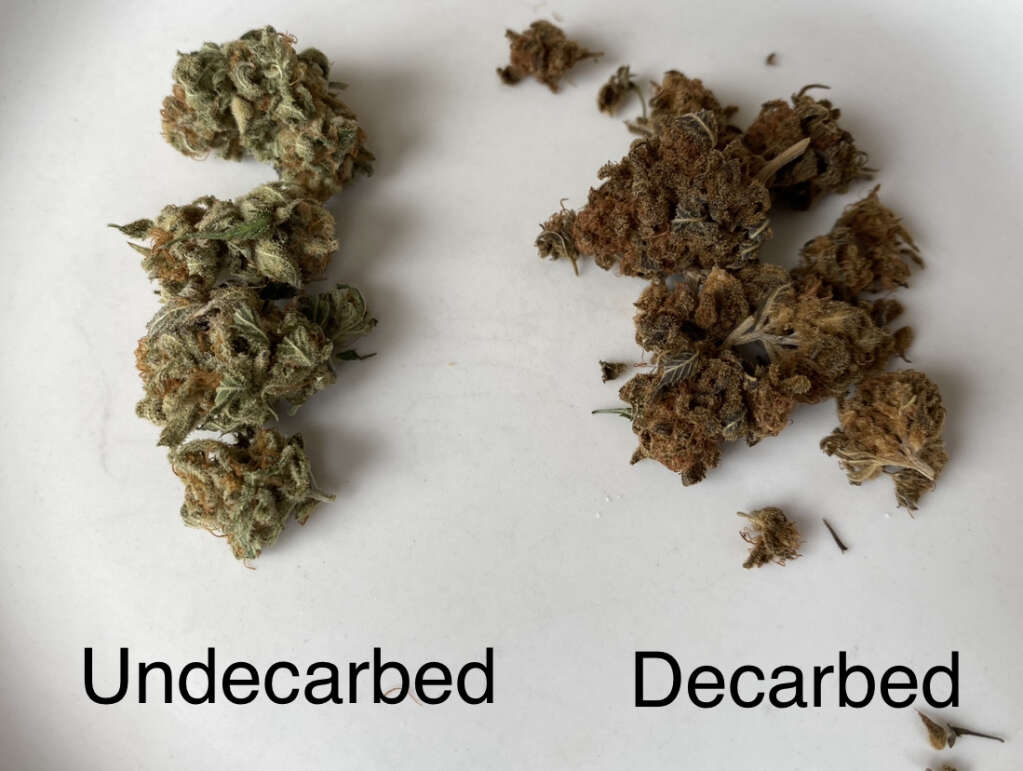

Decarboxylation – Commonly referred to as decarb, decarboxylation is the process of applying controlled heat over time to allow the cannabinoids to release their carbonyl groups of 2 oxygen atoms and one hydrogen atom.
Decarb transforms the molecular structure of cannabinoids from acid precursors (i.e. THCA, CBDA) to the neutral cannabinoids from cannabis we’ve learned to dose medicinally and recreationally (i.e. THC, CBD).
Example: THCA to THC
Dispensary – A place to legally buy products in a state that’s defied Federal laws and demanded the right to offer their citizens freedom to access marijuana.

Dosing – The action of administering medicine, typically in measured and controlled volumes.
Drying – Flowers and plant material can be used in many ways directly after harvest, but drying allows for longer storage times. Many of the processes used to create cannabis products require dry plant material.
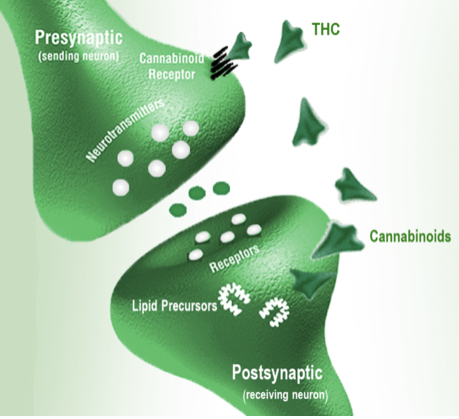
ECS – Acronym for the cellular signaling system we call the endocannabinoid system. The ECS balances your central nervous system with your immune system to keep your body humming along efficiently and energetically.
Edibles – Cannabis consumed like a food, including capsules, tinctures, beverages and more. Basically, any cannabis product that makes its way into the body through the stomach.

Endocannabinoids – The cannabinoids created inside your body.
Endocannabinoid System (ECS) – You body’s major cellular signaling system. All of your trillions of cells need to communicate effectively with each other to keep individual cells from falling out of harmony with their prescribed functions. The ECS does this by having enzymes produce/synthesize molecules called cannabinoids to modulate the flow of other signaling molecules. Then other specialized enzymes disassemble the used cannabinoids and clean up behind.
The goal of the ECS is creating homeostasis.
Endocannabinoid Tone – The overall harmonic tone your ECS creates when there are:
- enough endocannabinoid receptors,
- enough endocannabinoids,
- and enough enzymes that dismantle the cannabinoids after use (for easy elimination from the body) to keep the body systems in balance.
Entourage Effect – Cannabis produces an essential oil rich in dozens and dozens of medicinally-valuable components, among them cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. Each of these molecules on their own have value to the human healing forces, but combined they create a symphony of synergy, enhancing each other’s benefits so that the whole is more than the sum of the parts. We call this wonder of molecular interaction the entourage effect.
Enzymes – Molecules your body produces to create change in other molecules. It’s enzymes that metabolize cannabinoids, and they also tear cannabinoid molecules apart and prepare them to be flushed from the body.
Extraction – The process of stripping the essential oils from plants for further processing as recreational and medicinal products. With today’s technological advancements, some extractions can be done with or without solvents.
FECO – Full-plant extraction cannabis oil; extraction using the plant’s combined offerings, as opposed to isolating individual molecules like CBD or THC.
Grinder – A device used to break apart the tightly-packed dried buds.
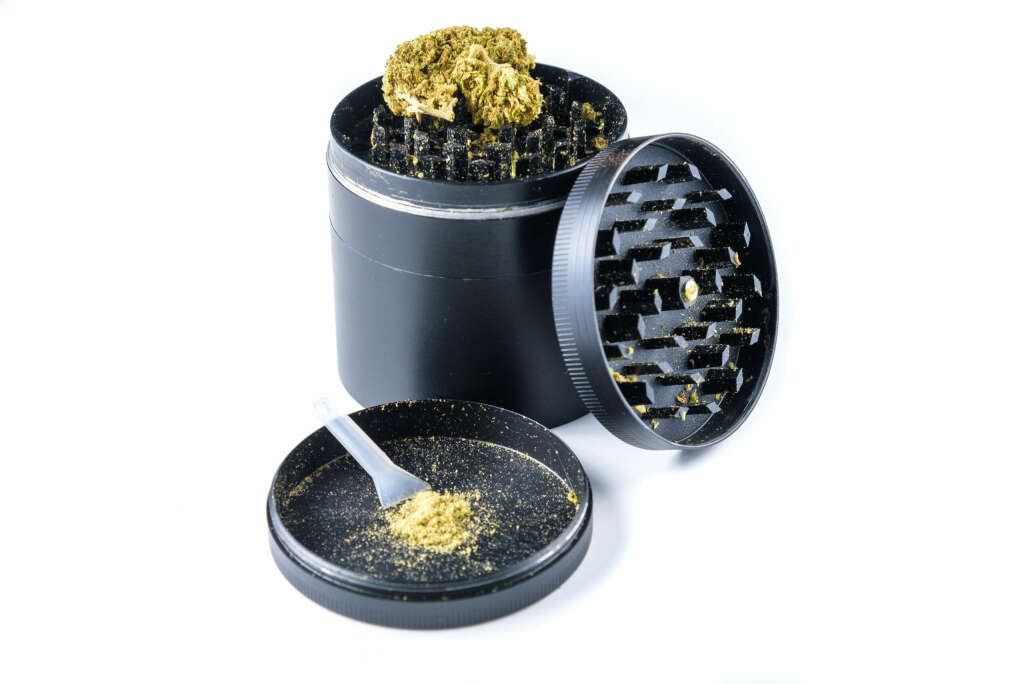

Grinders come in many shapes and sizes, some collecting kief in a lower compartment.
High – Another name for the buzz you get from weed containing THC. Being high is grossly misunderstood by those who have not experienced a cannabis buzz when it’s really nothing more than feeling better than you did when stress or pain was distracting you from the pleasure of being alive.
It’s a simple process to control how high you become with THC by either limiting your dose of THC or balancing it out with CBD.
Homeostasis – That balance point of your body systems where you are the best you can be- mentally, physically, emotionally, and spiritually. It’s the job of your ECS to keep the cells in homeostatic balance.
Infused cannabis oil – Flower buds and plant material simmered into a carrier oil to increase bioavailability and more efficiently control dose levels.
Joint – The most socially-recognizable form of cannabis consumption, a joint is comprised of ground, dry cannabis plant material – usually flower buds – rolled up in cigarette paper and smoked.

Kief – Dried and cured trichomes holding the trapped essential oils of the cannabis plant that have been mechanically separated from the plant material and collected.
Live Resin – An exciting development in resin production that freezes freshly-harvested plants and extracts the essential oils in a way that preserves more of the plant’s terpene profile, creating a more flavorful, satisfying experience and increased medicinal effectiveness.
Lipids – Molecules your body uses, among which we find cannabinoids.
Liquid Sunflower Lecithin – The liquid form of sunflower lecithin, an invaluable aid to increasing bioavailability of cannabinoids, particularly in edible and topical products.
Marijuana – When the U.S. government officials decided they were going to vilify the plant, they gave it this name as a means to create fear-mongering and social division.

MDR – An acronym for Medial Dorsal Rami, an attempt to name the area on the upper back where the vertebrae of the neck and torso meet, about C7/T1. This area is an alternate pathway for topicals that offers relief for certain conditions without getting you high.
NOTE: Some sensitive people may feel mild psychoactive effects while using this pathway.
Omega Fatty Acids – The fatty acids your body uses to create balance. The ECS uses omega fatty acids to create endocannabinoids. The human body runs most effectively when supplied with a 1:1 balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. The typical Western diet is out of kilter, with over six times as many omega-6, creating systemic inflammation as a tragic side effect of poor diet.
Onset – The moment following administration that you begin to feel the effects. Onset times will mostly depend on how well your body absorbs and what administration method you choose.
Phytocannabinoids – Cannabinoids created by plants, as opposed to those your body creates. Marijuana is unique in the plant kingdom in its ability to produce hundreds of different types of cannabinoids.

Pot – A popular name for Cannabis sativa.
Profile – The list of identified components found in a plant’s oil or a product made with oils. The profile would be the known cannabinoids and terpenes found in your product, determined by laboratory testing.
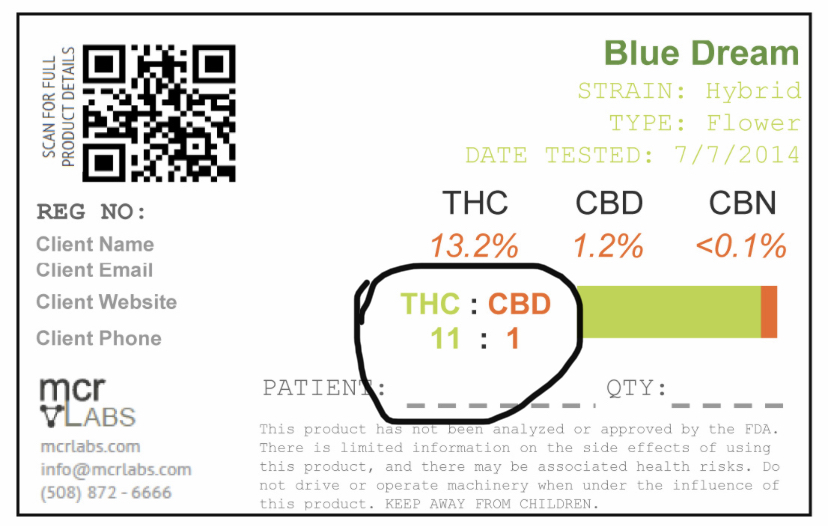
Ratio – The balance of cannabinoids (typically THC and CBD) found in a plant’s oils or a product made with its oils. The ratio will be listed on the product label in ratio form:
- 1:1 would be THC and CBD in equal balance.
- 2:1 means one of the two major cannabinoids is more strongly represented at twice the value of the other.
- 3:1 would mean one cannabinoid was represented at triple the value of the other.
Since we have yet to establish consistency in which cannabinoid is listed first on ALL labels, you want to be certain which number stands for which cannabinoid before you purchase. Your trusted budtender will help you properly identify them so you don’t get it backwards.
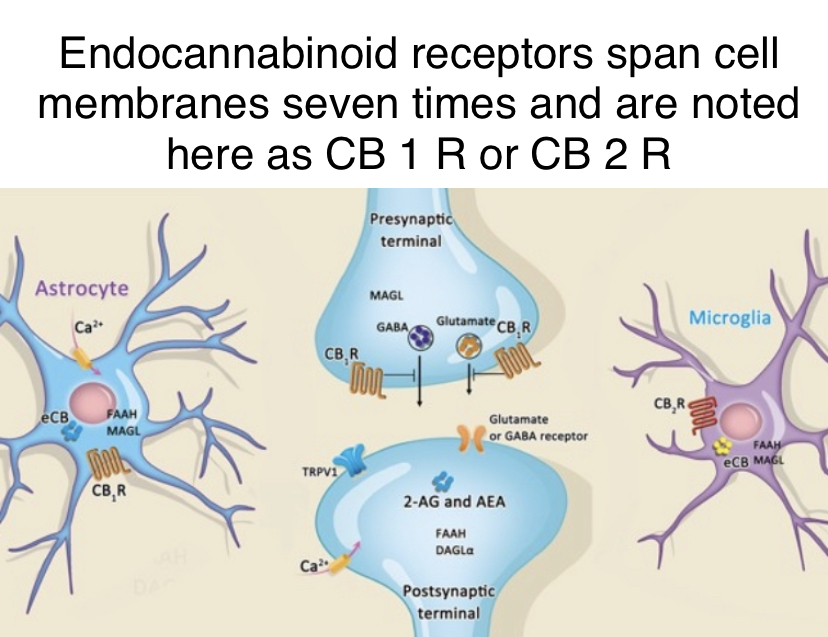
Receptors – Specialized proteins that span the cell membranes, their antenna-like projections connecting the inside of the cell with the outside atmosphere of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Receptors are triggered by specific signaling molecules to activate the chemical cascades inside cells, which modifies the internal atmosphere, and thereby the vibratory rate of that cell.
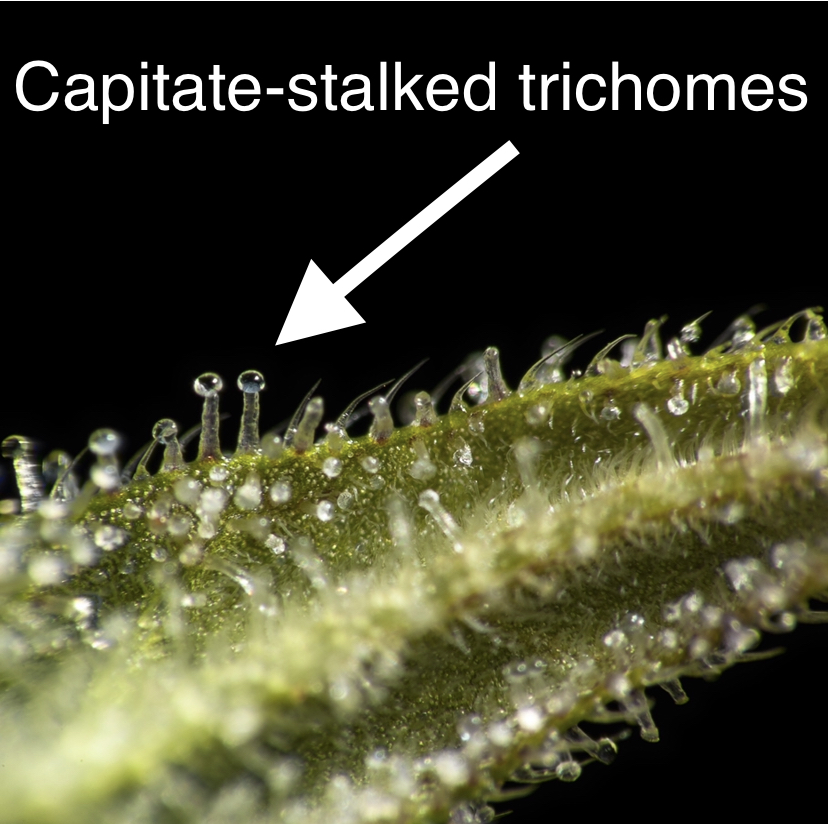
Resin – The essential oils of the cannabis plant, created in the plant’s trichomes containing the cannabinoids that act as a protective shield from potentially harmful sun’s rays and the terpenes that repel the onslaught of insects and grazing animals.
Resin is also the name used to describe the gooey oil residue that clogs bong down stems and pipe or bowl stems after prolonged use for smoking cannabis.
Rick Simpson Oil (RSO) – The concentrated oil of cannabis plants, popularized and promoted as a healing agent deluxe by Canadian citizen Rick Simpson. RSO is often identified as the impetus behind the current protocols of using concentrated cannabis oils for the treatment of human disease states.
Rosin – The oil from the trichomes of the cannabis plant, extracted from the plant without the use of solvents, but rather by using heat and pressure.
Terpenes – Fragrant and flavorful molecules, lighter than air, giving plants their wonderful perfumes and many flavors. Cannabis plants produce hundreds of terpenes in their profiles, a rare occurrence in the plant kingdom.
Terpenes themselves create a long list of beneficial effects in the human body and are widely used in aromatherapy. To a large extent, it’s the terpenes working in synergy with cannabinoids that create the many and varied ways people respond to cannabis products.
Topicals – Preparations intended to bring local relief by applying directly to the skin. Topicals can be in the form of oils, creams, salves, lotions, patches, or any other method used to treat through the skin.

Trichomes – Glandular resin glands covering the surface of cannabis plants, most strongly concentrated in the flower buds. Trichomes are the chemical factories that produce the essential oils of cannabis plants that we use for recreational and medicinal purposes.

Vaporizing – An alternative to combustion, vaporizing heats enough to release the vapors of the essential oils of the cannabis product without combusting, thus sparing you from breathing smoke into your lungs.
Weed – A popular name for Cannabis sativa.
We’ll continue to update this guide over time, but if there’s any terms you think we should add or if you have any questions- drop us a comment below!



